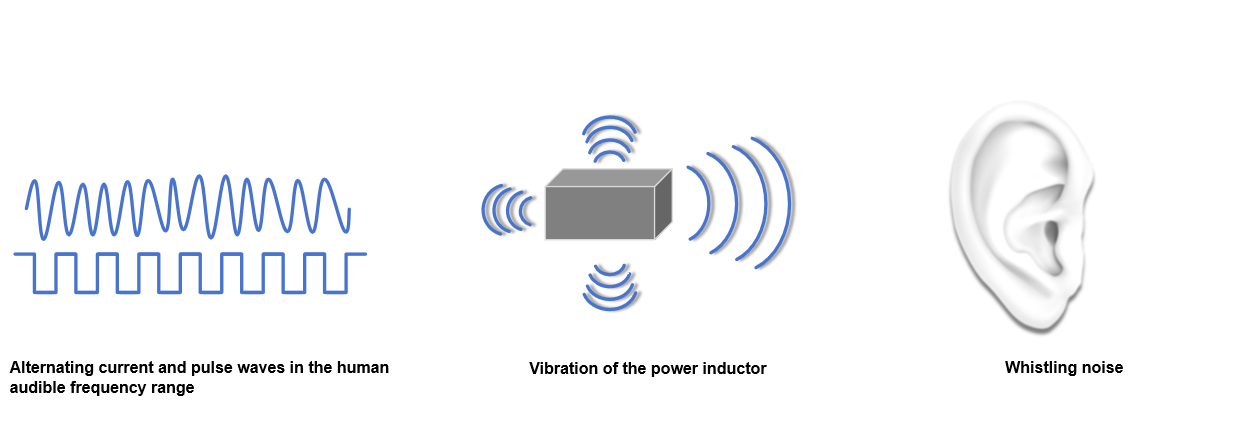
Power inductors are often used in DC/DC power conversion circuits. The pulsed current flowing through power inductors makes them one of the noise sources. However, the switching frequency ranging from hundreds of kilohertz to several megahertz is beyond the audible frequency range of the human ear.
In some special cases, if a pulsed current in the range of 20Hz to 20KHz flows through the inductor, the power inductor may vibrate, thus causing whistling noise.
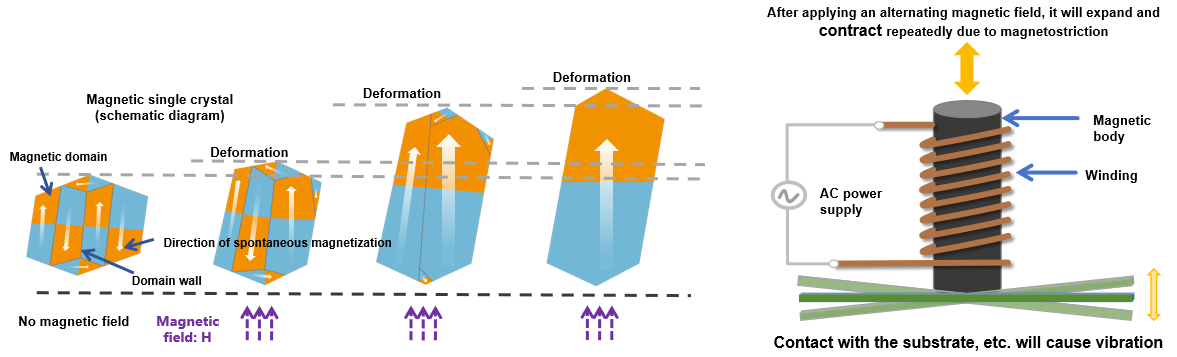
Magnetostrictive magnetic core
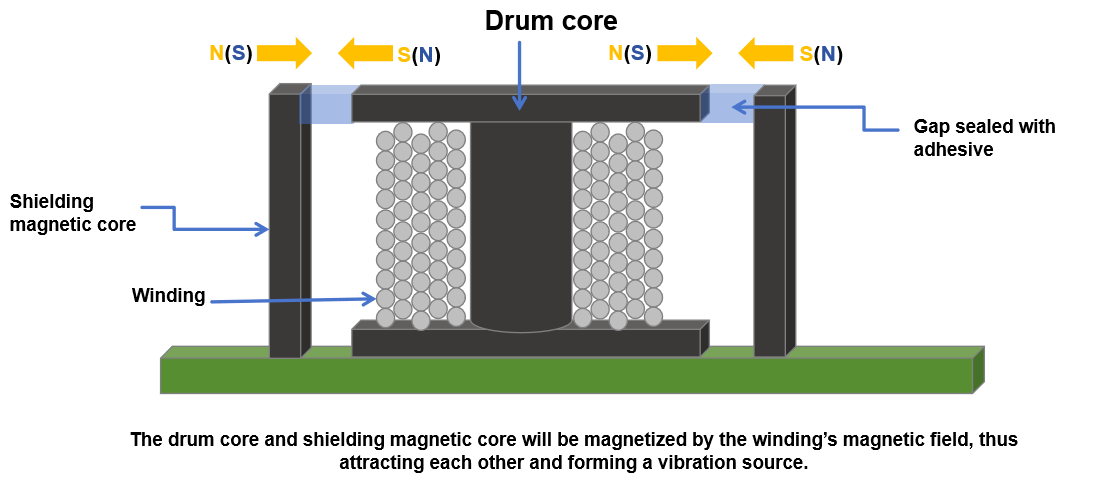
When the inductor is in operation, the magnetic core and the shielding magnetic core are magnetized and exhibit ferromagnetic properties, thus attracting each other and generating vibration.
There is a gap between the magnetic core and the shielding magnetic core, which is sealed with an adhesive; yet the adhesive cannot completely suppress the vibration caused by their mutual attraction.
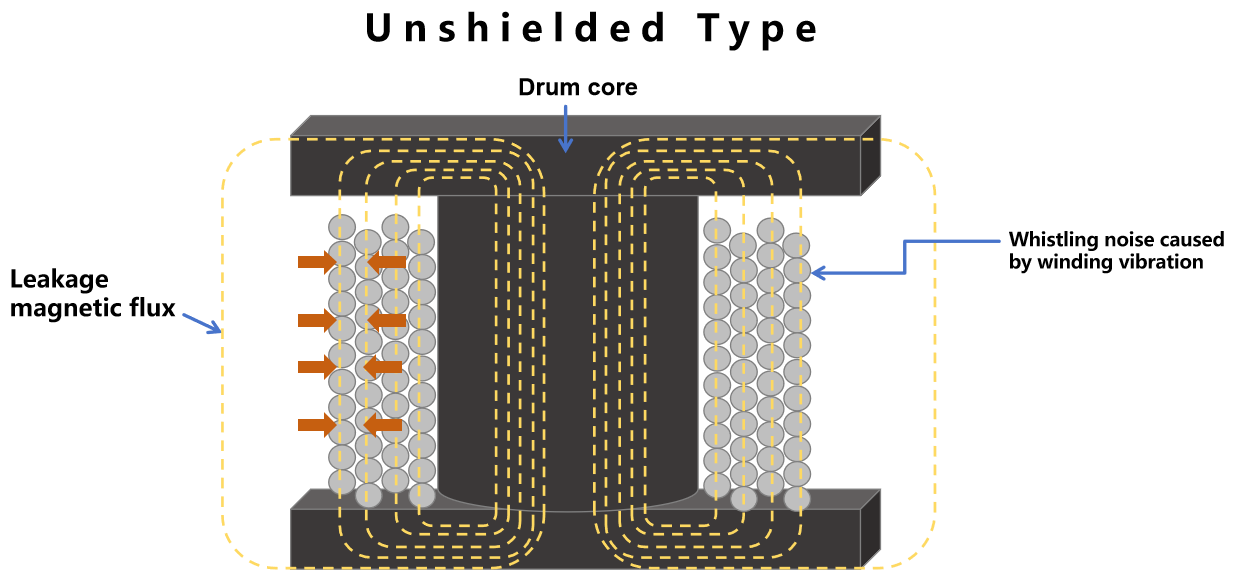
In the magnetic field generated by leakage magnetic flux, current flows through the winding; therefore, a force acts on the winding (in accordance with Fleming's Left-Hand Rule), causing the winding to vibrate and thus triggering whistling noise.

For a fully shielded inductor, the magnetic flux circulates inside the magnetic core, so there is almost no leakage magnetic flux.
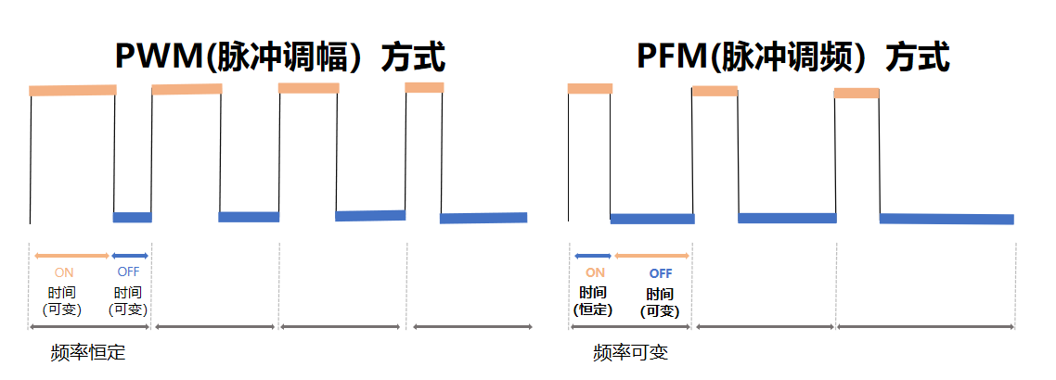
To reduce switching losses and improve conversion efficiency, the PMU switches from PWM mode to PFM mode under light-load conditions. When the electrical energy stored in the output capacitor is sufficient to supply the load and there is no need to charge the capacitor, the DC/DC circuit will not turn on again to charge the capacitor and supply the load until the stored electrical energy is consumed to a certain extent. This is equivalent to reducing the switching frequency.
Insufficient Anti-saturation Capability of Power InductorsDue to the insufficient anti-saturation capability of power inductors, the inductance drops sharply under high-current conditions. As a result, the peak current of the inductor exceeds the limit of the power management IC, forcing the switching transistor to turn off. The current on the inductor then gradually decreases, and the switching transistor turns on again when the circuit meets specific conditions. Once the frequency of the inductor current falls into the audio frequency band, the inductor may produce whistling noise.
Load FluctuationUnder non-fixed load conditions (e.g., power amplifier chips), the power required by the load is dynamically adjusted as needed. The power drawn by the load from the power supply fluctuates, which may cause the DC/DC converter to operate in an alternating state between DCM (Discontinuous Conduction Mode) and CCM (Continuous Conduction Mode), or put the supply voltage/current in a fluctuating state. When the fluctuation frequency is low, the inductor may generate whistling noise.
Whistling Noise Caused by PWM DimmingDuring PWM dimming of LEDs, if the frequency of the PWM signal is low and falls within the range of 20Hz to 20KHz, the pulsed current on the inductor will cause the inductor to vibrate, resulting in whistling noise.





